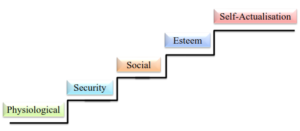
MASLOW’S NEED HIERARCHY
The most widely recognized theory of motivation is the needs hierarchy theory. Abraham Maslow suggested that people have a complex set of exceptionally strong needs, which can be arranged in a hierarchy. These needs are:
- Physiological needs
The physiological needs are at the top of the hierarchy because they tend to have the highest strength until they are reasonably satisfied. Until these needs are satisfied to the degree needed for the efficient operation of the body, the majority of a person’s activities will probably be at this level, and the other levels will provide him with little motivation. It includes hunger, thirst, shelter, sex and other bodily needs.
- Safety/Security
The needs for safety, stability and absence of pain, threat or illness are all security needs. Like physiological needs, unsatisfied security needs cause people to be preoccupied with satisfying them. Managers who believe that security needs are most important they focus on rules, job security and fringe benefits. Such managers may not encourage innovation by employees and will not reward risk taking. Employees who are most concerned about security will follow rules strictly.
- Social/Affiliation
After the first two needs are satisfied, social needs become important in the need hierarchy. Since man is a social being, he has a need to belong and to be accepted by various groups. When social needs become dominant, a person Will strive for meaningful relations With others. In organization context when affiliation needs are the primary source of motivation, people value the workplace as an opportunity for finding and establishing warm and friendly interpersonal relationships.
- Esteem
The esteem needs are concerned with self-respect, self-respect, a feeling of personal worth, feeling of being unique, and recognition. Satisfaction of these needs produces feelings of self-confidence, prestige, power and control.
- Self-actualisation
This level represents the culmination of all the lower, intermediate and higher needs of human. Self-actualisation is the need to maximize one’s potential. whatever it may be. This is related With the development of intrinsic capabilities which lead people to seek Situations that can utilize their potential. This includes competence which implies control over environmental factors, both physical and social. and achievement. A man with high intensity of achievement needs will be restless unless he can find fulfillment in doing what he is fit to do.
Assumptions of the theories :
- A satisfied need does not motivate. When one need is satisfied another need emerges to take its place, so people are always striving to satisfy some need.
- The needs network for most people is complex, with several affecting the behavior of each person at any one time.
- In general, lower level needs must be satisfied before higher level needs are activated sufficiently to drive behavior.
- There are more ways to satisfy higher level needs than lower level needs.
- Maslow need hierarchy is viewed as a simple and straightforward analysis of human motivation with human needs forming the basis for analysis. This theory has found wide acceptance among practicing managers for its logical exposition and easy to understand format.
- The theory points out a fact which ignored in the conventional approach to the management of people, that a satisfied need is not a motivator of behvaiour.
- Maslow has maintained a reasonably sensible and realistic view of human nature. He has insisted that process of self actualization cannot occur automatically as it requires initiatives, desires and efforts on the part of the individuals.
Demerits
- The hierarchy of basic needs is not always fixed. Different people may have different orders. For example, in case of creative people like singers, painters etc. their self actualization needs may become the dominant motivation force even before their lower order needs are satisfied.
- There is lack of direct cause and effect relationship between need and behavior. Thus a particular need may cause behavior in different ways in different persons.
- The level of satisfaction for particular need may differ form person to person. A person tries for his higher level need when his lower order need is reasonably satisfied.