Direction/Directing
Meaning, Definitions, Features, Importance, Principles, Techniques and Models
Directing/Direction
Meaning
After planning, organizing and staffing functions are completed in the context of a work cycle, directing function begins. Every manager in the organization gives direction to his subordinates as superior and receives direction as subordinate from his superior.
Direction is the process in which the managers instruct, guide and oversee the performance of the workers to achieve predetermined goals. Infact managers play a significant role in direction by directing their subordinates the way they should do their work to achieve organizational objectives. It takes place after planning, organizing and staffing. Directing can either lead to success or failure.
Definitions
According to Haimann
Direction is the process and technique of issuing instructions and making certain that operations are carried out as planned.
According to Newman and Warren
Direction actively dealing with the steps a manager takes to get subordinates and others to carry out plans.
According to Marshall
Directing involve determining the course, giving order and instruction and providing dynamic leadership”.
According to GR Terry
Direction means activating and moving into action-supplying simulative power to the group.
According to Earnest Dale
Direction is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the best of their ability.
Features of Direction
1. An important managerial function.
2. Performed at every level of management that means it is all pervasive and the manager at every level provides guidance and inspiration to his subordinates.
3. A continuous process as it is required throughout the left of the organization
4. Is initiated at the top level and followed to bottom through hierarchy.
5. Serves dual purpose
6. aims at getting things done by subordinates,
7. to free superiors for other important work.
Human factor is predominant in the managerial function of direction. Since direction is to instruct human beings, who are emotional unpredictable and complex; it becomes all the more important and essential. Therefore, it is suggested to adopt delicacy sobriety while tackling with human beings.
Direction is a creative activity and it helps in converting plans into performance. Without proper direction, people may become inactive and the Organizational resources may also get wasted.
Importance of Direction
Direction Plays an important role as every action is initiated through direction, which can be seen as follows
(i) Initiates Actions
All the actions required to accomplish organizational objectives are initiated through director. All the human and non-human resources are to be dealt deftly and intelligently to make a profitable organization. Other managerial activities like planning, organizing, staffing become inactive without direction. Every organization is the sum total of human and non-human resources and to achieve efficiency, it is important to handle them efficiently.
(ii) Integrates Employees’ Efforts
It has been observed that no organization or no department works in isolation but each individual’s performance affects the performance of others in the organizations. So, individuals not only need to be effective also, which can be achieved through direction.
(iii) Enhances Individual’s Performance
The three essential elements of direction-Motivation, Leadership and Communication play an important role in tapping the potential of an individual and influencing him to perform effectively.
(iv) Brings Change
Direction facilitates changes in the organization as organizations exist in society and society keeps changing. All the changes whether external or internal are incorporated and implemented through direction only. It can be achieved with the help of three elements of direction : Motivation, Leadership, Communication.
(v) Brings Stability and Balance
Direction provides stability, harmony, balance to work effectively for a longer period; which is attained only by three essential elements of Direction, i.e., Motivation, Leadership and Communication. Marshall Dimock calls direction the heart of administration. He finds high correlation between direction and work performance.
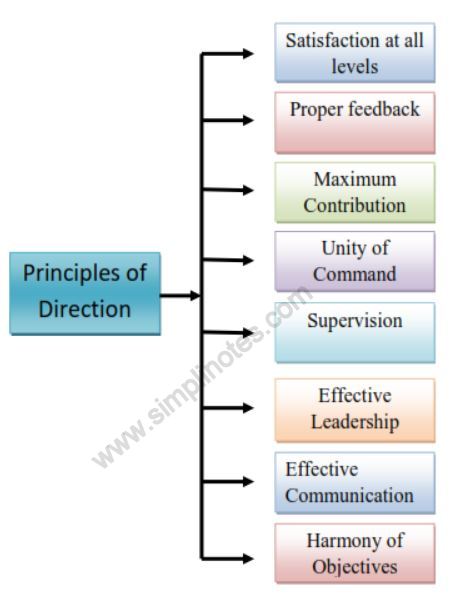
Principles of Direction
- It should be of such kind that leads to maximum individual contribution.
- It should be in such a way that it streamlines and integrate both organizational and individual objectives.
- It should not affect them adversely rather should provide adequate satisfaction.
- It should be from one superior and should report to the same.
- It should be properly chosen out of these three techniques- authoritarian, consultative and free-rein; depending upon the nature of superior and subordinates and the situational variables.
- It should be given through proper communication skills. Thus, effective communication between superior and subordinate is the key to direction.
- It should be given in comprehensive and understandable way as direction is: what to do, how to do, when to do? Clear instructions enable the subordinates to get clear situation and avoid unnecessary queries and explanations from superior.
- It can be given through informal channel as it has been confirmed that these channels are more effective. It becomes the responsibility of manager to understand, spot and make use of such informal channels.
- It should be given by adopting effective leadership styles. Thus, managers need to become leaders so that they can influence the activities of their subordinates without dissatisfying them.
- It should be checked and proper feedback has to be taken to understand the difficulties their subordinates are facing and the orders can be modified and replaced, if needed.
|
Direction |
Supervision |
|
| 1 | Newman and Warren defined direction actively dealing with the steps a manager takes to get subordinates and others to carry out plans. | Terry and Franklin have defined supervision as “guiding and directing efforts of employees and other resources to accomplish stated work outputs.”
|
| 2 | Direction is much more wider as compared- to supervision. | Supervision is limited as compared to direction.
|
| 3 | It includes motivating, leading and communicating with employees. | It does not include these three elements. |
Techniques of Direction
1. By giving Orders and Instructions
A manager can adopt this technique of giving orders and instructions. He conveys the nature of work processes and procedures adopted and timing of job performance. It has to be well understood by the subordinates what work they should do, how they should do, and when they should do through this technique.
2. By Monitoring
It is very necessary to take the follow-up of the instructions/orders given by the manager to know whether the subordinates have carried out orders and instructions properly or not. There can be reasons like they might not have understood clearly, they might not have adequate resources, there might be contradictory orders creating confusion; of not carrying out the instructions properly. If needed, the manager may withdraw, amend, change the orders or may provide further explanations and help his subordinates to accomplish them.
3. By following Organizational Rules and Policies
Most of the organizations formulate certain guidelines, set some norms, rules and regulations, on them and do not feel the need of giving any extra instructions and orders. This happens more in the case of routine work and special instructions are given only for special assignments.
4. By understanding Subordinates Behavior
Some managers adopt this technique of understanding their subordinates’ behavior, capabilities and select the pattern of directing accordingly. Majorly, these are three behavioral patterns-Autocratic, Participative and Free-rein. In autocratic, the superior gives instructions in detail but does not involve his subordinates at all in decision-making process.
In participative, decision making is a joint-process between the superior and his subordinates; detailed instructions are not required. In free-rein pattern, the superior does not provide orders and instructions at all; only the broad guidelines for taking the right decision are provided. Now, it depends on the skill of superior understanding the subordinates’ behavioral pattern and making it possible with that.

thanku sir/madam for this amazing notes