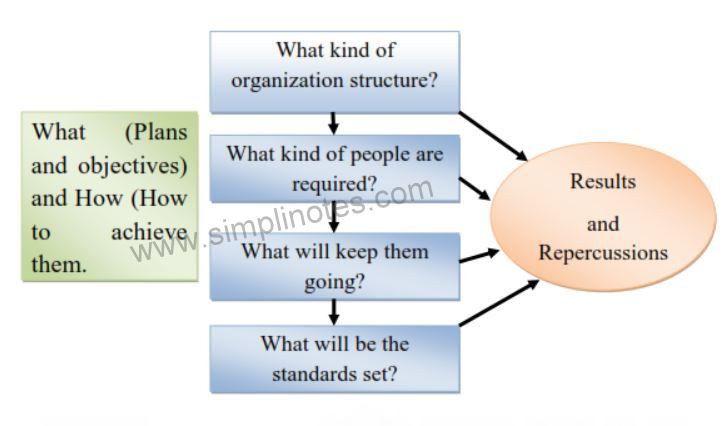
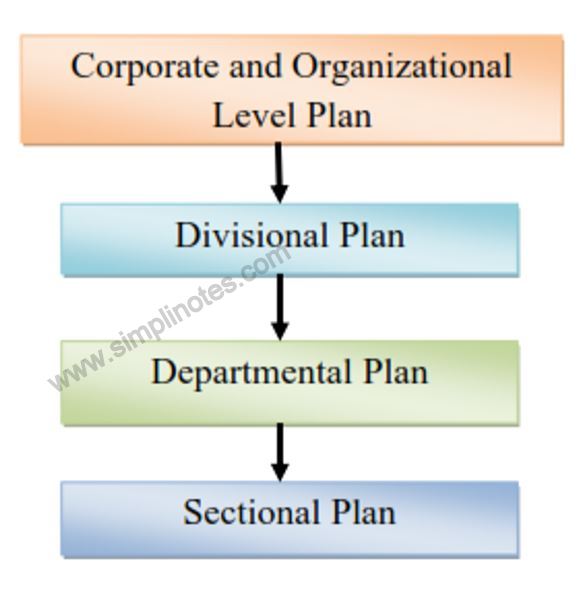
Planning
Meaning, Nature, Features, Types, Process and Barriers
Planning
Planning involves the determination of future course of action. It is a mental process requiring the use of intellectual faculties, foresight and sound judgement. It is one of the basic managerial functions.
Definitions of Planning
According to Koontz and 0′ Donnell
“Planning is deciding in advance what to do, how to do and who is to do it. Panning bridges the gap from where we are to where we want to go. It makes it possible for things to occur which would not otherwise happen”.
According to Farland
“Planning may be broadly defined as a concept of executive action that embodies the skills of anticipating, influencing and controlling the nature and direction of change”.
According to Franklin
“Planning is selecting the formation and making assumptions regarding the future to formulate activities necessary to active organisation objectives”.
In short planning is preparing today for tomorrow. It is the activity that allows managers to determine what they want and how they will achieve it.
Features of Planning
After defining and understanding the concept of planning following features can be deduced about the main function of management.
i. Planning is a process rather than behavior at a given point of time. This process determines the future course of action.
ii. Planning is primarily concerned with looking into future. It requires forecasting of future situation in which the organization has to function. Therefore correct forecasting of future situation leads to correct decisions about future course of actions.
iii. Planning involves selection of suitable course of action. This means that there are several alternatives for achieving a particular objective or set of objectives. However all of them are not equally feasible or suitable for the organization.
iv. Planning is undertaken at all levels of the organization because all levels of management are concerned with future course of action. However its role increases at higher levels of management.
v. Planning is flexible as commitment is based on future conditions which are always dynamic.
vi. Planning is pervasive and continuous managerial function involving complex processes of perception, analysis, conceptual thought, communication, decision and action.
Nature and Characteristics of Planning Management
Planning has some unique characteristics of its own which separate it from other managerial functions.
1. Primacy of Planning
- Planning is the first and foremost activity of managerial functions.
- Planning gives foundation for all other functions like organizing, staffing, directing, controlling, etc.
- All functions are performed to achieve the objectives set by the planning process, this can be presented as follows.
2. Pervasiveness of Planning
- Planning is pervasive and extends throughout the organization the organization. Every manager has a planning function to perform.
- The style, the span and the content of planning vary at different levels as top level management’s area is quite widen as compared to the lower and middle level of management. The decisions taken by the top level personnel affect the organization more as compared to the low level management. Some examples of planning are Production Planning, Inventory Planning, Financial Planning, Project Planning etc.
3. Future Oriented
Planning is a process which focuses at future and make plans to tackle the future events. The managers need to consider the situations, the constraints, the facilities, the resources within and outside the organization to make a good plan.
4. Based on Information
It is not possible to have a good plan without proper, accurate and timely information. Not only latest information but the information about the past and thinking about the future is equally important.
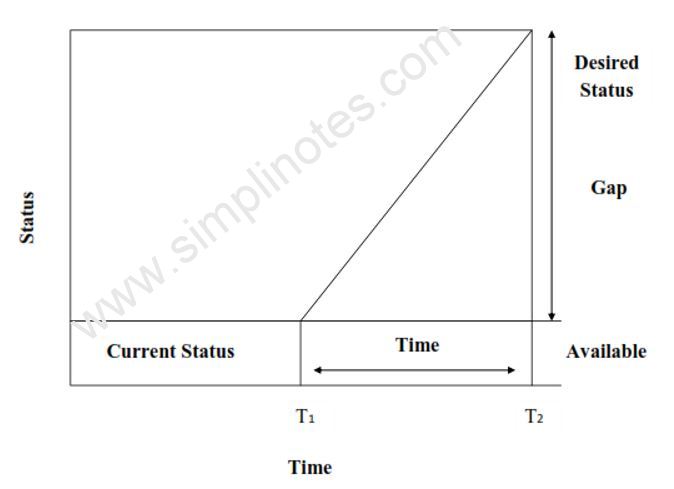
5. A Rational Approach
Planning is a rational approach for defining where one stands, where one wants to go in future and how to reach there. Planning as a rational approach tries to fill the gap between current status and desired status.
6. Formal as well as Informal in Nature
- Although, planning is formal affair but may be done informally.
- Formal planning is done through investigation by analysis of various factors and is a step by step process which proceeds very logically.
- Informal planning is done by the managers concerning day to day activities through the word of mouth and is quite flexible in nature.
7. Intellectual Process
- The manager has to have the ability to think in a logical way and understand things to plan effectively.
- The manager has to have ability to viz problems, and analyse them and find the suitable solutions for them.
- The manager has to have the ability to view the coming opportunities and threads in the near future.
- The manager has to have the ability to choose the right course of action.
8. Action Oriented
- Although, it is an intellectual process but it needs practical, flexible and sensible way of action rather than fixed ideas or theories.
- Planning follows action, therefore, they need to be practical, flexible and implementable.
9. Decision Making
Planning involves decision making based on organizational policies, programmes, strategies, objectives, other plans and procedures.
10. Dynamism
- Planning is a dynamic process and it is based on the external and internal changes of environment.
- Every organisation needs to modulate its practices to streamline itself with the current trend.
- It is a continuous, never ending process of assessment and reassessment of goals, resources, directions, opportunities and problems of the organisation.
11. Open System Approach
Planning is an open system approach and while adopting open system approach in planning managers have to take into account the dynamic features of the environment.