Methods and Machinery for the settlement of Industrial disputes
Lasting industrial peace requires that the causes of industrial disputes should be eliminated. In other words, preventive steps should be taken so that industrial disputes do not occur. But if preventive machinery fails, then the industrial dispute settlement machinery should be activated by the government because non- settlement of disputes will prove to be very costly to the workers, management and the society as a whole.
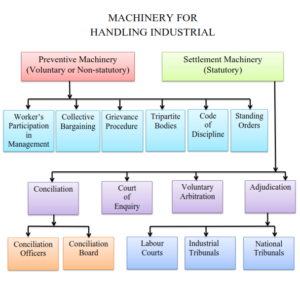
The machinery for handling of industrial conflicts has been shown in the following figure.
A. Prevention of Industrial Disputes
The preventive machinery has been set up with a view to creating harmonious relations between labour and management so that disputes do not arise. It comprises of the following measures:
- Worker’s participation in management
- Collective bargaining
- Grievance Procedure
- Tripartite bodies
- Code of discipline
- Standing orders
- Worker’s participation in management
It is a method whereby the workers are allowed to be consulted and to have a say on the management of the unit. The International Labour Organisation has been encouraging member to promote the schemes of worker’s participation in management. The important schemes of worker’s participation are:
i. Work committee
ii. Suggestion scheme
iii. Joint Management Councils
iv. Worker Directors
v. Co-partnership
- Collective bargaining
Collective bargaining is a process in which the representatives of the employer and the employees meet and attempt to negotiate a contract governing the employer. Collective bargaining not only includes negotiation, administration and enforcement of the written contracts between the employees and the employers, but also includes the process of resolving labour management conflicts. Collective bargaining is democratic, flexible, pragmatic and durable means of regulating industrial relations.
- Grievance Procedure
It is established for an early settlement of worker’s grievances. In India, a Model Grievance Procedure was adopted by the Indian Labour Conference in its 16th session held in 1958. At present, the Indian industries are adopting either the Model Grievance or procedures formulated by themselves with modifications in the Model Grievance Procedure.
In India, Sec. 9-C of the Industrial Disputes Act provides that in every industrial establishment employing twenty or more workmen shall have one or more Grievance Redressal Committee for the resolution of disputes arising out of individual grievances.