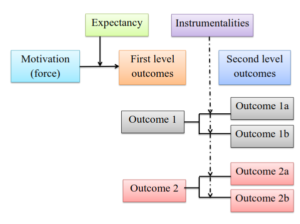
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory of Motivation
Expectancy model was developed by Victor Vroom in 1964. Criticizing the content theories of motivation which are based on the needs of people and their priority. Vroom has presented an alternative theory which is based on motivation process. Various theories which are based on motivation process are more concerned with the cognitive antecedents that go into motivation or efforts and more important with the way they relate to each other.
Vroom’s expectancy theory has its roots in the cognitive concepts of pioneering Kurt Lewin and Edward Tolman and in the choice behavior and utility concepts of classical economic theory. According to Vroom. people will be motivated to do things to achieve some goals to the extent that they expect that certain actions on their part will help them to achieve the goal. The theory is based on the simple equation :
Motivation (force) = Expectancy X Instrumentality X Valence
Vrooms expectancy theory is presented below:
As shown in the figure above the model is built around the concepts of valence, instrumentality and expectancy. Therefore this model is referred to as VIE theory. The various terms related to this model are explained below :
Valence
Valencce menas the strength of an individual’s preference for a particular outcome. Other terms that might be used are value, incentive, attitude and expected utility. Valence is positive when the individual prefers attaining the outcome to not attaining it. Valence is negative when the individual prefers not attaining the outcome to attaining it and it is zero when the ondovidual is indifferent towards the outcome.
Instrumentality
Another major input into the valence is the instrumentality if the first level outcome in obtaining second level outcomes. For example the person would be motivated towards superior performance because of the desire to be promoted, The superior performance (first level outcome) is seen as being instrumental in obtaining a promotion (second level outcome).
Expectancy
Another major variable in the Vroom motivational pocess is expectancy. Expectancy relates efforts to first level outcomes and second level outcomes. In other words, expectancy in Vroom’s theory is the probability that a particular action or effort will lead to a particular first level outcome.
Assumptions
1. Individuals join an organization with clear expectations of their needs, motivation and environment.
2. Individual behavior is typically their conscious decision.
3. Individuals seek to fulfill different goals and needs through their organisation.
4. Individuals like to choose among the alternatives in order to optimize their outcome
Merits
1. It recognizes individual differences in work motivation and suggests that motivation is a complex process as compared to Maslow’s or Herzberg’s simplistic models.
2. It also clarifies the relationship between individual and organizational goals.
Demerits
1. Vroom’s theory indicates only the conceptual determinants of motivation and how they are related. It does not provide specific suggestions on what motivates organizational members as the Maslow, Hezberg and Alderfer models do.
2. The theory is complex and its validity cannot be fully tested.
3. The theory cannot be applied in practice.