Air Pollution
Depending upon the generation of different air pollutants, they are grouped as
- Primary Pollutants
- Secondary Pollutants
1. Primary Pollutants
A Primary Pollutant can be defined as a harmful chemical that directly enters the air as a result of either man made or natural activities.
There are 5 major primary air pollutants which together contribute more than 90% of world’s air pollution.
i. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
It is colourless, odourless, tasteless gas,chemically inert under normal conditions of temperature and pressure. It has no effect at normal concentration (0.1 ppm) but at higher concentrations it seriously affects the human metabolism.
Sources
- Natural processes such as volcanoes, natural gas emission.
- Electrical discharge during cloud forming, seed germination march gas production etc. contribute in atmosphere though in small amounts.
- Transportation contribute 64% of CO in air.
- Forest fires and agricultural burning contributes about 17% of CO in atmosphere.
- Industrial processes such as electric furnance and blast furnances in iron and steel industry, petroleum refining, paper industry, gas manufacture and coal mining etc. causes about 9.6% of CO in air.
Effects
- Reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood by selectively combining with haemoglobin (Hb) forming carbozyhaemoglobin (COHb). This causes giddiness, laziness and exhaustion.
- It reduces vision and causes cardiovascular disorders.
- CO is a very dangerous asphyxiant and its high levels are fatal to human life.
Another oxide of carbon is carbon dioxide. It is the basic end product obtained on the burning fossil fuels, paper, leaves and other carbon containing material. Carbon dioxide is used by plants for photosynthesis. Although carbon dioxide has no direct effect on health, but with higher concentrations it causes global warming, acid rain and greenhouse effect.
ii. Nitrogen Oxides
The group include eight possible oxides nitrogen, NO, NO2, and N2O primarily involved in air pollution. NO is a colourless, odourless gas, but NO2 is reddish brown and have suffocating odour. NO and NO2 are formed as:
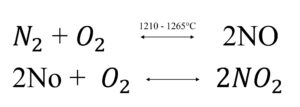
The formation of NO occurs at high temperature. The second reaction is also favoured at high temperature about 1100C°. NO2 is also formed by photolytic reaction.
