3. Analysis of transactions
TA is a technique for examining the nature of interpersonal communication between the two individuals and to analyse its effectiveness. Every piece of conversation is treated as a transaction. Every person transacts from all the three ego states but each one of us has one ego state as dominant. Transaction is effective when stimulus and response is from the same ego state and complementary in nature. Crossed transactions create conflict and problems for interpersonal behaviour. Depending upon the ego states of persons involved in transactions, there may be three types of transactions – complementary, crossed and ulterior.
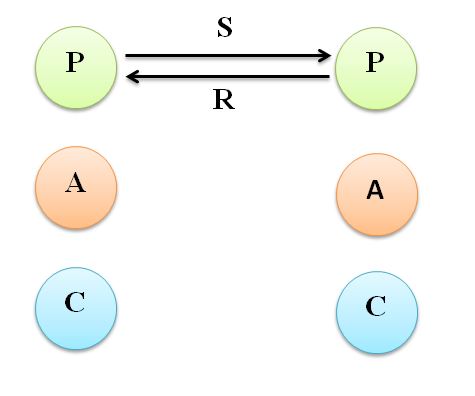
(a) Complementary Transactions
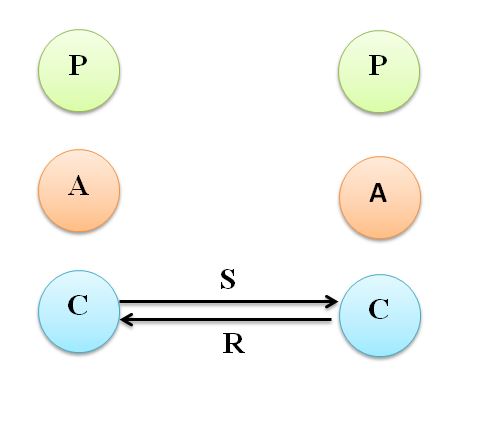
A transaction is complementary when the stimulus and response patterns from one ego state to another are parallel. Thus, the message by a person gets the predicted response from other person. In all, there can be nine complementary transactions. These are adult-adult, parent-child, child-parent etc. The transaction is complementary because both are acting in the perceived and expected ego states. Usually in such a case, both persons are satisfied and communication is complete. These complementary transactions are elaborated as follows.–
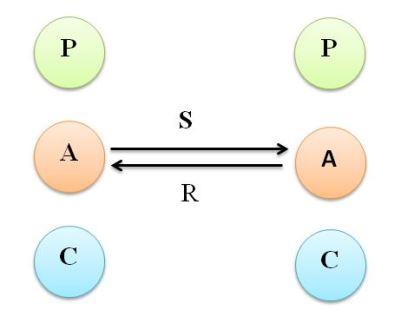
1. Adult-Adult Transaction
Both individuals are transacting from adult ego state. The stimulus and response are based on logical thinking and rationale. This type of communication is considered most ideal in any organization. There is least chance of conflict among the workers.
2. Adult – Parent Transaction
In adult – parent ego state, manager speaks from adult ego state which is rational and backed by rules and regulations while the employees speak from the parent ego state which is authorization, is not likely to smooth in the long run. Parent ego state (workers) will try to control and dominate the manager. The employees may develop hostile attitude towards the boss.
3. Adult – Child Transactions
Adult-child interaction can be effective when the manager is aware of the ego state of the employee. In such a case, the manager can allow the employee in the child ego to be creative. But there may be problem in this interaction when the employee acts irrationally because of his child ego. Another problem in this context may be in the form of assumption of employee’s ego that may be taken in adult ego but this assumption may not hold good. This creates a situation that may be frustrating to the manager and the employee.
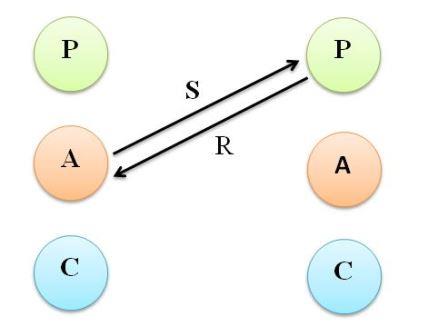
4. Parent-Parent Transaction
The manager in the parent ego uses ‘I am O.K. you are not O.K.’ life position. He will be source of admonitions. Rewards, rules. Criticisms, praise. The parent-parent transaction can be beneficial in cases where employee joins forces with the manager and supports him. There are certain disadvantages of this type of situation. this m ay lead to unnecessary competition between the manager and the employee because the latter will promote his own ideas rather than those of manager.
5. Parent-Adult Transaction
The boss is transacting from parent ego while his subordinate is responding from adult ego state. Such type of relationship may not last long. The manager may be frustrated because the employee will not perform as directed. At the same time, the employee may also feel frustration because of manager’s failures to act as adult. Due to frustration, such a relationship may not last long.
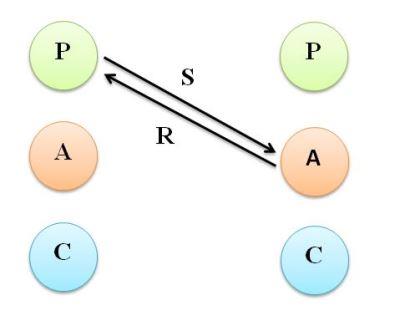
6. Parent-Child Transaction
This transaction is workable in the organization where the manager will get the work done from subordinates by advising, guiding, and by assigning rewards for good work and punishment for non-performance. The subordinates (Child ego) will listen to manager and look forward for advice, guidance, and assistance at each stage of production cycle. Manager may get frustration because he may develop the feeling that he is controlling an inefficient work force.
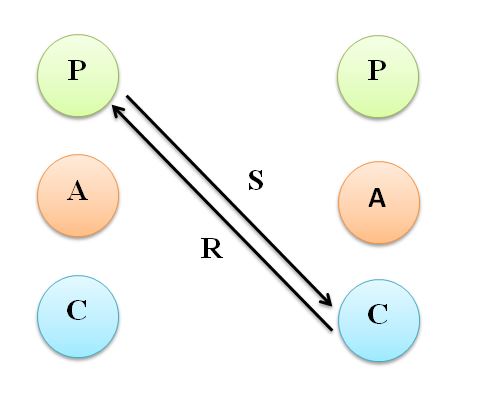
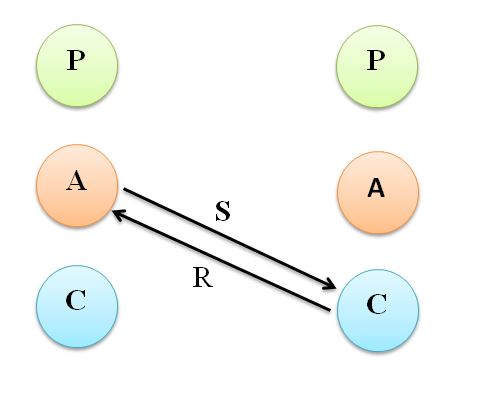
7. Child – Parent ego state Transactions
This is not a very effective style of communication whose manager has a child ego state and employee’s parent ego state. In such situation employees would control the manager. The latter would always perceive employees as threat and look forward for their advice from time to time. It will be lassie-faire type of command. Instances of manager being ridiculed and talked about loosely by subordinates will be a common phenomenon.
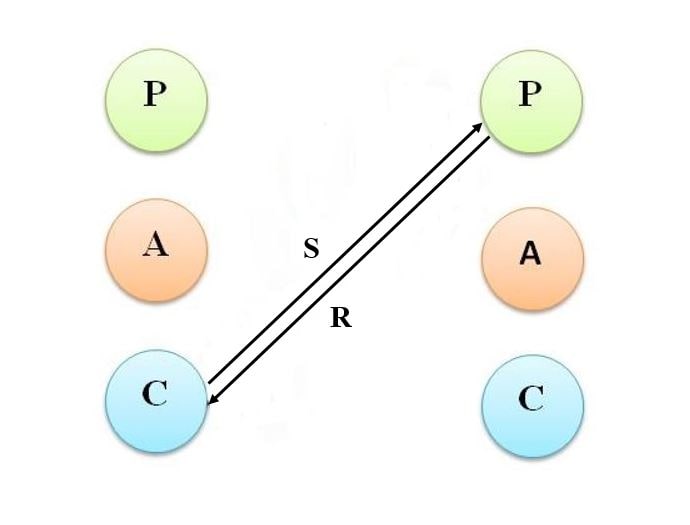
8. Child – Adult ego state Transactions
When manager acts from child ego, there will be poor decisions based on whims and fancies and emotions. This will pose a problem for employees who want to work rationally. Unless the ego state of the manager is changed, this is going to be problem in the organization. No growth can be expected with child ego manager at the helms of affairs.
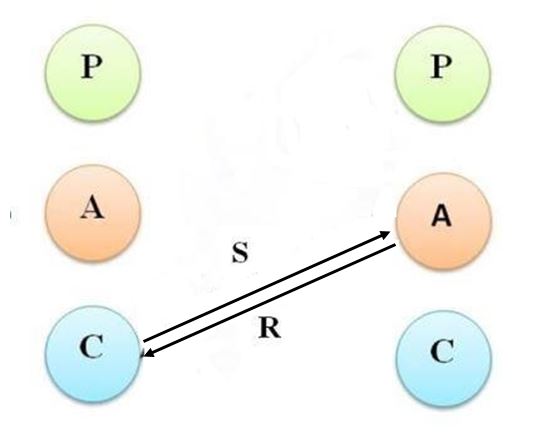
9. Child- Child Transaction
The manager interacting in child-child egos is not capable of leading his employee successfully and proves to be a liability to the organisation. This transaction may not be lasting because the organisation will review performance both manager and employee are acting on whim and fancy, consequently jeopardizing the organisational performance.
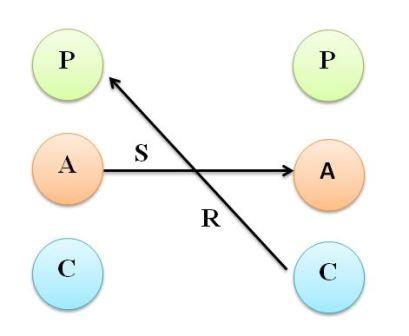
(b) Non-Complementary Transactions
Non-Complimentary or crossed transactions are those transactions in which a sender sends the message on the basis of his ego state, but the response is from an uncompatible ego state on the part of receiver. Such behaviour occur when stimulus and response is not parallel. Following figure depicts non-complimentary transaction. In this, the manager tries to deal with the employee on adult-adult bass but the employee responds on child-to-parent basis and the communication is blocked. Crossed transaction is not satisfactory one because the line of communication is blocked and the further transaction does not take place. In such case the manager might refuse to play parent-child game and may try again for an adult communication. Another alternative for manager may be to move parent-child state in order to resume communication with the employee.
(c) Ulterior Transactions
Ulterior transactions are most complex transactions because if involves more than two egos states working at the same time with double meaning in the stimulus. This type of transaction is very common i.e. diplomatic circles when you say something but mean the other. Thus, the real message is often disguised in a socially acceptable way. On the surface level, the communication has a clear adult language, whereas on the psychological level it carries a hidden message. Just like crossed transactions, ulterior transactions are also undesirable.
4. Script analysis
In a layman’s view, a script is the text of a play, motion picture or radio or TV programme. In TA, a person’s life is compared to a play and the script is the text of that play. When confronted with a situation, a person acts according to his script which is based on what he expects or how he views his life position. Berne has contributed most to the understanding of life script. To him,
“Script is a complete plan of living, offering both structures-structure of injunctions, prescriptions and permissions, and structure which makes one winner or loser in life.”
According to Jongeward, life script resembles the script of drama—characters, dialogues, actions and scenes, themes and plays, culminating towards a climax, and ends in final curtain. She also uses the concept of a person’s two stages for action—the public stage and the private stage. McClelland provides a scientific study of life script of people who has studied the relationship between stories heard and read by children and their motives in living. His researches have shown that achievers’ scripts are based on the success stories while the scripts of power oriented persons are based on stories of risk.6 A person, when confronted with a situation, acts according to his script which is based on what he expects or how he views his life position. In a sense, man’s behaviour becomes quasi-programmed by the script which emerges out of his life experience. This life position of persons affects his interaction with others. From this point of view, the analysis of life positions is an important aspect of TA.
5. Psychological Games
Psychological games are set of transaction, which has following characteristics:-
(a) Transactions are repetitive
(b) Transactions tend to make sense on superficial or social level.
(c) One or more transaction has ulterior value.
The set of transactions, which has negative pay offs, prevent people/organizations becoming winners. Psychological games are played by individuals to fill up time, provoke attention and re-enforce early opinion about self and others to fulfill a sense of destiny. Game players usually assume one of three basic roles: persecutor, victim, or rescuer, persecutors are characterised by such people who make unrealistic rules, enforce rules in cruel ways, and pick on little guys rather than people of their own size. Victims are people who provoke others to put them down, use them, and to hurt them; send them helpless messages, forget conveniently, and act confused. Rescuers are characterised by people who offer helpfulness to keep others dependent on them, do not really help others and may actually dislike helping, and work to maintain the victim role so that they can continue to play rescuer. These three roles are not independent, rather the players of psychological games often switch back and forth in their roles.
Reasons for Psychological Games
i. To get Strokes
ii. To Strengthen Psychological Positions.
iii. To Avoid or Control Intimacy
Methods of Preventing Games
Psychological games are not good as they prevent open, warm and intimate relationship. These must be discouraged. Jongeward has suggested the following steps to overcome the psychological games:
(a) Avoidance of complementary hand.
(b) Avoidance of victim role
(c) Avoid putting other people down.
(d) Avoidance of putting one-self down.
(e) Practice giving positive strokes in all transactions and avoidance of negative strokes.
(f) Investing more of life’s time in activities of intimacy.
(g) Leveling of thinking with others.
6. Study of life positions
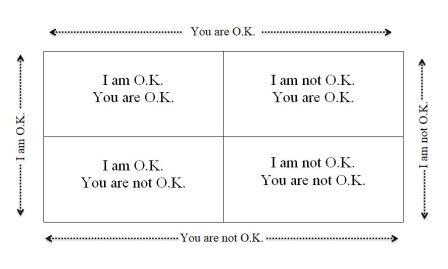
In the process of growing up, people make basic assumptions about their own self worth as well as about the worth of significant people in their environment. These assumptions tend to remain with the person for life, unless major experiences occur to change them. Harris called the combination of assumptions about self and the other person, a LIFE POSITION. They into four categories as shown in figure below:
(i) I am OK, you are OK
(ii) I am OK, you are not OK
(iii) I am not OK, you are OK
(iv) I am not OK, you are not OK.
i) I am OK, you are OK
This is an ideal life position because this position is rationally chosen one. An individual achieve this life position after having large number of O.K. experiences with others. People feel happy and life is worth living. Individual with this life position expresses confidence in his subordinates, work with high level of delegatation of authority, and believes in give and take. Manages enjoys good communication network, work with confidence and there is work sharing and positive attitude towards work. People remain happy and have high level of job satisfaction. People work with adult ego state. There is no conflict situation and there is total understanding among subordinates and peer group. An Ideal life position.
(ii) I am OK, you are not OK
This is distrustful psychological life position taken by individual who feel that others are wrong. They blame others for their failure. People who have been neglected by parents in their childhood take this position. They generally operate from rebellion child ego state that feel victimized and blame others for their miseries. Mangers lack trust, confidence in the intellectual level, skills and talent in their subordinates and do not believe in delegation of authority. They perceive delegation as threat to their personal existence. Managers are critical, oppressive and point out flaws in the working of subordinates. They operate from critical parent ego state and rarely give positive remarks. They feel their workers lazy, irresponsible and find them as stated in theory X of Mc Gregor. People with this life position express bossy attitude.
(iii) I am not OK, you are OK
This position is common to persons who feel powerlessness in comparison to others. It is based on one’s feelings about oneself. Individuals who feel a clear distinction between themselves and the people around them who could do many thing! that the individuals could not do, hold this life position. Persons with this life position always grumble for one thing or the other. ^Managers operating from this position tend to give and receive bad feelings. They often use their bad feelings as an excuse to act out against others, and when the whole thing comes full circle even they feel guilty for their acts and turn their bad feelings against themselves. They tend to vacillate in their behaviour and are often unpredictable and erratic.
(iv) I am not OK, you are not OK
This is a desperate life position. This position is taken by those people who lose interest in living. They feel that life is not worthy living at all. In extreme cases, they commit suicide or homicide. This is the case of individuals who are neglected seriously by their parents and are brought by servants. Managers operating from this position are likely to get put down strokes from others. They do not make decisions in time, make stupid mistakes or otherwise provoke others to give them negative reactions. They lack personal potency, look to others for final decisions, and delegate inappropriately.
On analysis, it is seen that everybody has elements of various life position. But one of the four-life positions is dominant. “I am okay your are okay” is the best life position All- individual must try and modify life position in various situations. Adult – adult transaction from the above life position and positive life script will make an outstanding manager.
7. Stroking
Stroking is an important aspect of transactional analysis. Stroking is an act of implying recognition to other person. Stroking is recognition that a person gives to his subordinates for good work done or even bad work done. Lack of stroking has an adverse psychological and physiological effect on individual. Stroking is a basic unit of motivation that can be seen from the following :
(a) The quantity and the quality of strokes serve as either positive or negative motivation for employees.
(b) Good share of psychological satisfaction we get from work is from strokes available from other persons.
(c) We get strokes from the work itself. There are positive and negative strokes. Positive strokes are recognition, pat on the back and affection shown by superiors, who make subordinate feel okay. It is the recognition of the work that employees get boost to do even better. Negative strokes on the other hand are the feeling “you are not okay” conveyed by superiors by way of criticism, hating and by scolding for the job not done well. It serves as negative encouragement and a feeling of failure is created among the workers. Negative strokes received by individual also serves as positive strokes because an individual who has done a mistake expects a negative stroke from his boss, so that mental tension is relieved and a social equilibrium is achieved in the relationship. When the work is challenging, the worker gets an ultimate satisfaction from the work itself that serves as a motivator. It is therefore necessary that managers/supervisors assign to their subordinates the work, which, in itself is rich and has a motivational value. Positive strokes must be used as frequently as possible.
Benefits and Uses of TA
Following are some of the specific areas where TA can be applied beneficially:
1. TA is applied to bring positive actions from people because TA brings positive approach towards life and hence positive actions. TA brings a clear change from negative feelings—confusion, defeat, fear, frustration, loneliness, pessimism, and suppression—to positive feelings—clear thinking, victory, achievement, courage, gratification, decision, friendship, optimism, and fulfillment. Such a change from negative attitude to positive attitude is a source of psychic energy.
2. With the help of TA people can understand their own personalities. It can help them understand why people sometimes respond as they do. With the help of TA, a manager can understand when a cross communication occurs and he can immediately take steps to convert into complementary communication. As a result there will be improvement in interpersonal communication.
3. Transactional analysis is basically applied to improve motivation of employees. When applied, it satisfies the human needs. Enrichment of job is achieved by helping fellow workers thereby achieving intrinsic value. It helps to change management style from theory X to Theory Y whose transformation takes place from parent – Child relationship to transaction involving adult – adult relationship, from “I am Okay, you are not okay to I am Okay – You are okay life positions.
4. TA can help in organisation development process. Jongeward has identified the role of TA in six areas of organisation development: to maintain adult-adult transactions, to give an OK to the natural child, to identify and untangle quickly crossed transactions, to minimise destructive game playing, to maximise encounters (intimacy), and to develop supportive systems, policies, and work environment. TA can be compared with managerial grid of Blake and Mounton, a technique for adopting appropriate leadership styles and organisation development. a technique for adopting appropriate leadership styles and organisation development. Various leadership styles may be described in terms of life positions, ego states, and transactions. For example, the 9—1 manager uses parent-child transaction, the 1-9 manager acts from child ego state, the 9—9 manager acts from adult ego and effectively makes use of parent and child ego states. In the managerial grid, 9—9 style is the most desirable which corresponds with adult-adult transaction which is best according to TA.
Besides these major areas, TA can be utilised anywhere the people come to interact. Jongeward has suggested that transactional analysis is a practical and useful interrelationship model for organisations because:
i. it is easy to learn,
ii. it gives a positive communication tool that is practical and almost immediately usable,
iii. it helps to increase a person’s on-the-job effectiveness because of better self- understanding and greater insight into personalities and transactions,
iv. it may help solve personal and family problems,
v. it gives a common language for people working together to attempt to solve their own communication problem,
vi. it is a non-threatening approach to self-evaluation, and
vii. It offers a method for analyzing not only people but also organizational scripts.
